Category: Parkinson’s Post
gLIDe Study: A Study to Assess the Safety and Effectiveness of Pridopidine Compared to Placebo in the Treatment of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesia in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03922711) The University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC) Department of Neurological Sciences is always looking to bring clinical trials with new drug development to our patients with Parkinson’s disease. We feel this is important because it not only provides much needed help in development of new drugs for patients with this disabling …
What is Deep Brain Stimulation therapy? Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgery or therapy is a treatment where a pacemaker type device is inserted into a patient’s brain with Parkinson’s disease (PD) to improve their motor symptoms or physical symptoms. DBS surgery consists of placing a wire with the tip in the deep part of the brain; the wire exits the skull through a hole and runs under the skin down into the chest where a pacemaker type battery is placed …
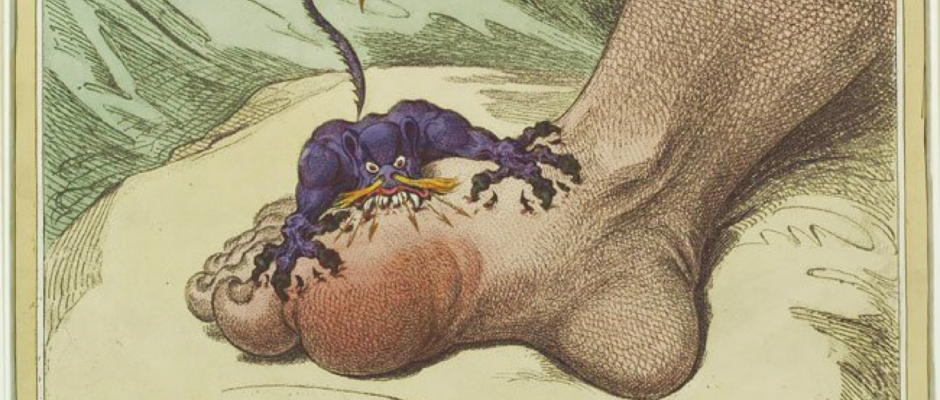
In this article, we will continue where we left off in the last newsletter in terms of research and neuroprotection in Parkinson’s Disease. This article may be read separately but is a continuation of the theme of neuroprotection research in Parkinson’s Disease. Gout, the unwalkable disease, was first identified by Egyptians nearly 2,600 years BC, but the most famous reference is to the description by Hippocrates in the Fifth Century B.C. whose aphorism for Gout still hold true. Over the …
The biggest efforts in Parkinson’s Disease (PD) have been to figure out ways to slow down this condition and then down the road consider ways that will stop or even potentially reverse the progression of Parkinson’s Disease. These efforts have been underway for more than 20 years starting as early as 1980s with attempt with vitamin E in high doses (DATATOP Study) along with selegiline a newly discovered agent at that point. Those efforts failed and vitamin E was found …
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease, with a life time risk of 4 percent. However, risk increases with age with a prevalence of one percent at age of 65 but rising to 20 percent after the age of 80 (Jane A. Driver. Neurology 2009) One out of twenty patients, is however, diagnosed before the age of 40. Parkinsonism alone is associated with a two-fold increase in the risk of death with a significant impact on mobility …
Parkinson Disease is a Neuro-degenerative disease which means that it is seen due to gradual loss off neurons or brain cells in certain parts of the brain. This process starts years before the diagnosis and an estimated 60% or more of the brain cells are lost before clinical diagnoses of Parkinson’s disease can be made due to motor symptoms. Once this process is initiated it continues on its own pace, which is different for each patient. Once this was recognized …